Nuclear Medicine Technologists
Certified Nuclear Medicine Technologist (CNMT), Nuclear Cardiology Technologist, Nuclear Medicine Technologist (NMT), Staff Nuclear Medicine Technologist
What they do:
Prepare, administer, and measure radioactive isotopes in therapeutic, diagnostic, and tracer studies using a variety of radioisotope equipment. Prepare stock solutions of radioactive materials and calculate doses to be administered by radiologists. Subject patients to radiation. Execute blood volume, red cell survival, and fat absorption studies following standard laboratory techniques.
On the job, you would:
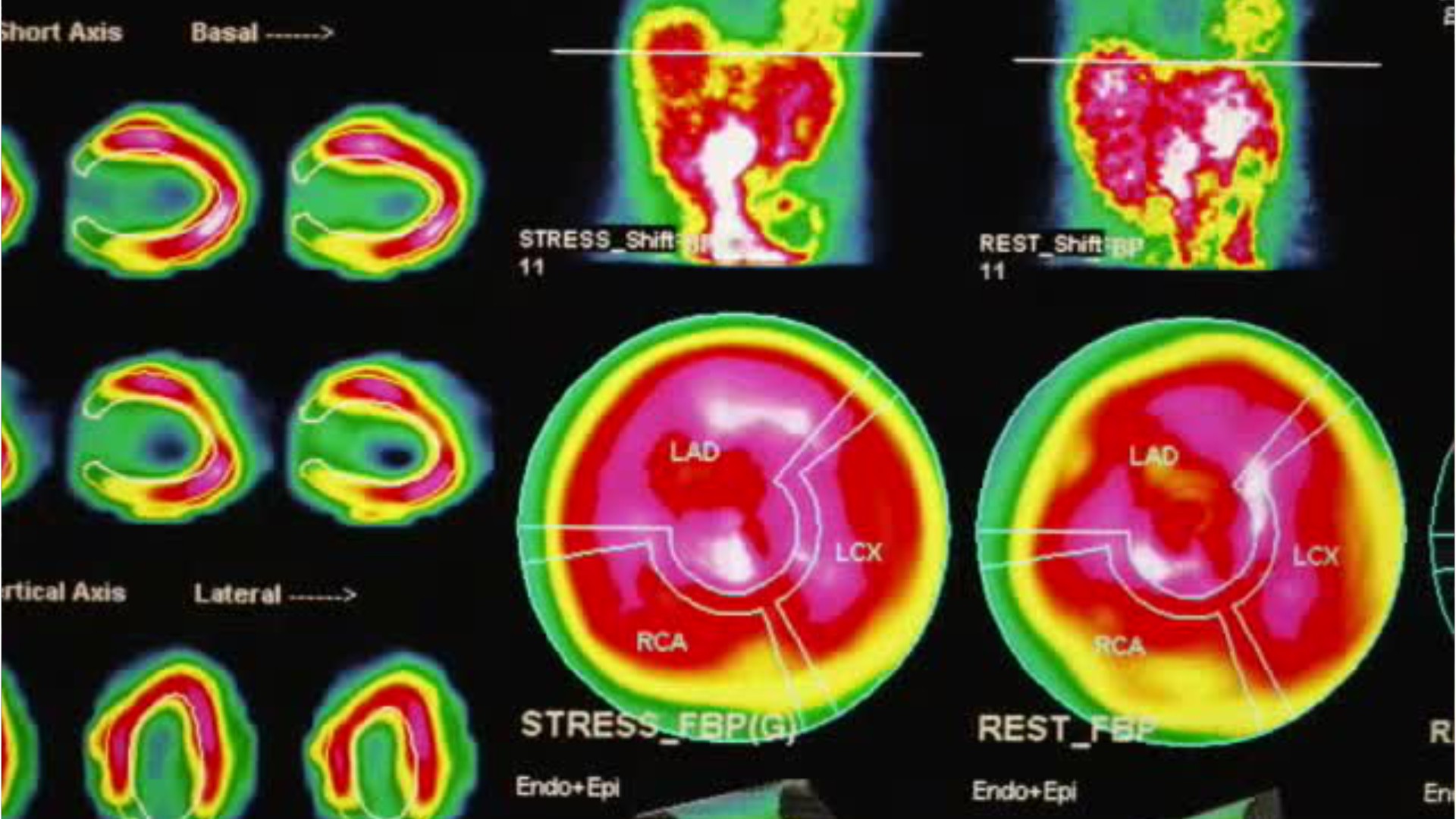
- Administer radiopharmaceuticals or radiation intravenously to detect or treat diseases, using radioisotope equipment, under direction of a physician.
- Detect and map radiopharmaceuticals in patients' bodies, using a camera to produce photographic or computer images.
- Process cardiac function studies, using computer.
Knowledge
Business
- customer service
- administrative services
Math and Science
- biology
- physics
Arts and Humanities
- English language
Health
- medicine and dentistry
Skills
Basic Skills
- thinking about the pros and cons of different ways to solve a problem
- listening to others, not interrupting, and asking good questions
Problem Solving
- noticing a problem and figuring out the best way to solve it
Social
- understanding people's reactions
- changing what is done based on other people's actions
Abilities
Verbal
- communicate by speaking
- listen and understand what people say
Ideas and Logic
- notice when problems happen
- order or arrange things
Math
- add, subtract, multiply, or divide
- choose the right type of math to solve a problem
Personality
People interested in this work like activities that include practical, hands-on problems and solutions.
They do well at jobs that need:
- Attention to Detail
- Concern for Others
- Dependability
- Cooperation
- Independence
- Integrity
Technology
You might use software like this on the job:
Medical software
- Electronic medical record EMR software
- MEDITECH software
Presentation software
- Microsoft PowerPoint
Spreadsheet software
- Microsoft Excel
Education
Education: (rated 3 of 5)
associate's degree or
bachelor's degree
usually needed
bachelor's degree
usually needed
Job Outlook
Below Average
New job opportunities are less likely in the future.
Explore More
- Cardiovascular Technologists & Technicians
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technologists
- Medical & Clinical Laboratory Technologists
- Radiation Therapists
- Radiologic Technologists & Technicians
You might like a career in one of these industries:
See more details at O*NET OnLine about nuclear medicine technologists.